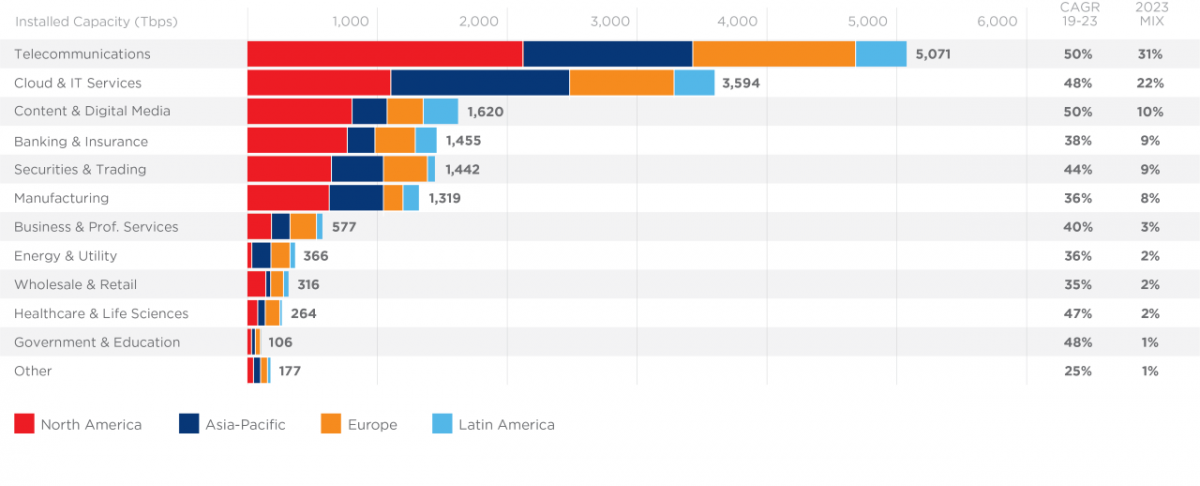
According to this, the fourth volume of the report (Vol.4), digital service providers, within industries like telecommunications, cloud & IT services, content & digital media and technology providers, are forecast to increase private connectivity bandwidth 5x by 2023, driven by greater demands from enterprises to close digital gaps at the edge.
As the pandemic continues to accelerate the shift to digital, enterprises facilitating more remote working, such as telecommunications and cloud & IT providers, are expected to contribute to 54% of the total interconnection bandwidth growth in EMEA, outpacing other industries in the region. Frankfurt, Amsterdam, Paris and London are predicted to be the top metros in Europe for interconnection bandwidth growth, with the region as a whole expected to account for 23% (3,782 Tbps) of the projected global installed interconnection bandwidth.
The report also forecasts that overall interconnection bandwidth—the measure of private connectivity for the transfer of data between organizations—will achieve a 45% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) from 2019 to 2023, within the EMEA region. In London, interconnection bandwidth is expected to grow at the same CAGR as the wider EMEA region, to 1,337 Tbps. This growth is at least three times higher than Paris, and more than twice that of Amsterdam. This supports London’s vital position as a strategic interconnection hub for digital business looking to compete on a global scale, despite the UK’s recent departure from the European Union.
The expected growth is driven by digital transformation, and specifically by greater demands from enterprises extending their digital infrastructure from centralized locations to distributed edge locations. This comes as businesses scale and support real-time interactions by strategically interconnecting workflows closer to, and across people, things, locations, cloud and data. The capacity of this connectivity is equivalent to 64 zettabytes of data exchange, which is enough bandwidth for every human on the planet (7.8 billion) to transmit their full DNA sequence in an hour.
Vertical/Industry Insights:
The GXI Vol.4 provides insight on how global macro trends and COVID-19 have impacted certain industry segments:
- Digital adoption patterns are changing in response to massive disruptions
- According to the GXI Vol.4, the digital adoption pattern has altered, with service providers now forecast to provision more interconnection bandwidth (10,284 Terabits per second (Tbps) by 2023) than enterprises, by a factor of nearly 2x.
- However, much of this service provider demand is anticipated to be in support of enterprises that are prioritizing their digital transformation in preparation for post-pandemic recovery.
- The report also predicts that enterprises with a digital infrastructure will extend their competitive advantage and continue to lead in business growth, while those without have struggled and are dependent on service providers to transform their business models.
- Traditional businesses are moving workloads to an edge-first architecture
- The GXI Vol.4 predicts that traditional business, within industries like banking & insurance, manufacturing and business & professional services, will represent a combined 30% of global interconnection bandwidth by 2023. This is led by the growing need to move workloads to the digital edge while scaling core IT infrastructure. By 2023, these traditional businesses are expected to reach a peak interconnection bandwidth growth rate of 50% annually.
- Healthcare & life sciences and government & education are expected to lead the traditional enterprises in their interconnection growth rate as public and private initiatives on artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are forecast to drive a combined 47% CAGR in interconnection bandwidth from 2019 to 2023.
- Organizations are benefiting from the “network effect”
- Organizations are maximizing their digital advantage by building a presence in locations with the most users, largest number of providers and the densest activities, known as the “network effect.” According to IDC, 80% of digital leaders will see the impact of connecting to multiple ecosystems, including improving their value to end customers by 2025.[1]
- The need for application exchange in digital ecosystems to support real-time engagement is essential and creates a network effect for businesses. The GXI Vol.4 predicts that connectivity from service providers to networks and cloud & IT service providers will be the two main sources of ecosystem interconnection, with an estimated 49% combined CAGR from 2019 to 2023.
The GXI Vol. 4 delivers insights by tracking, measuring and forecasting growth in interconnection bandwidth—the total capacity provisioned to privately and directly exchange traffic, with a diverse set of partners and providers, at distributed IT exchange points inside carrier-neutral colocation data centres.